Before learning about recursive copy lets go through the copy command first.
What is Copy command in mac?
“cp” command is used to copy the files from source directory to destination directory in mac. If we are using this “cp” command without any arguments as below, it can only copy the specific file. It won’t copy the complete directory.
cp <sourceFile> <destDir> // can copy only specific fileTo copy the entire directory along with its all content to the destination directory we need to use the argument as “-R” with copy command as “cp -R”
This -R with copy command is known as recursive copy.
How to copy complete directory in mac using recursive copy command.
Use the below recursive copy command to copy the complete directory and its contents.
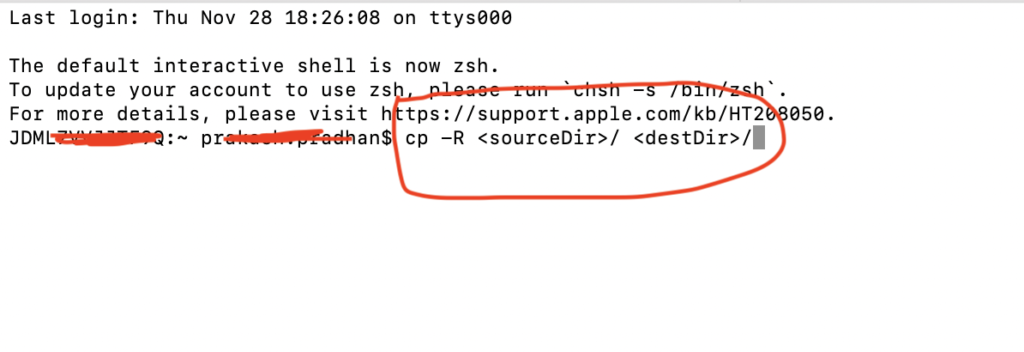
% cp -R <sourceDir> <destDir>The -R flag causes cp to copy the folder and its contents. Note that the folder name does not end with a slash, which would change how cp copies the folder
If we’re only seeing the files under the sourcedir being copied (instead of sourcedir as well), that’s happening because we kept the trailing slash for sourcedir
% cp -R <sourcedir>/ <destdir>The above only copies the files and their directories inside of sourcedir. Typically, if we want to include the directory we’re copying, we need to drop the trailing slash:
% cp -R <sourcedir> <destdir>
“CP” Permission denied error on mac.
Sometime while copying the files using copy command we can see the “permission denied”. so by using the below command we can allow the permission to these files for copy.
chmod 755 fileName
Here we don't want to give everyone rwx on the directory because we can create a security risk. And we wouldn't want to -R the chmod because that would write changes recursively.
so Just chmod 755 "filename" is ok.
Here's a break down of the numbers:
Read = 4
Write = 2
Execute = 1
Then you have 3 groups:
Owner.
Those who belong to the Group.
Everyone else.
So, if we want to give the owner rwx, those who belong to the group rw, and everyone else rw we just have to add the permissions: rwx = 7, because r+w+x is 4+2+1 and rw = 6 because r+w = 4+2.
How to move files in mac from source directory to destination directory.
Go to the Terminal app on your Mac.
Use the “mv” command to move files or folders from one location to another on the same computer. The mv command moves the file or folder from its old location and puts it in the new location.
For example, to move a file from your Downloads folder to a myfiles folder in your Documents folder:
% mv ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents/myfiles/file.txt
We can also change the name of the file as it’s moved:
% mv ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents/Work/newName.txt